Yup, you heard that right. A computer that’s as old as A.D. exists. Of course, it’s not a computer you’d be using to check the latest tweets, take a deep dive into a niche subreddit, or FaceTime your grandma. This computer had navigation functionality, helping ancient people discover new worlds and traverse this great planet.
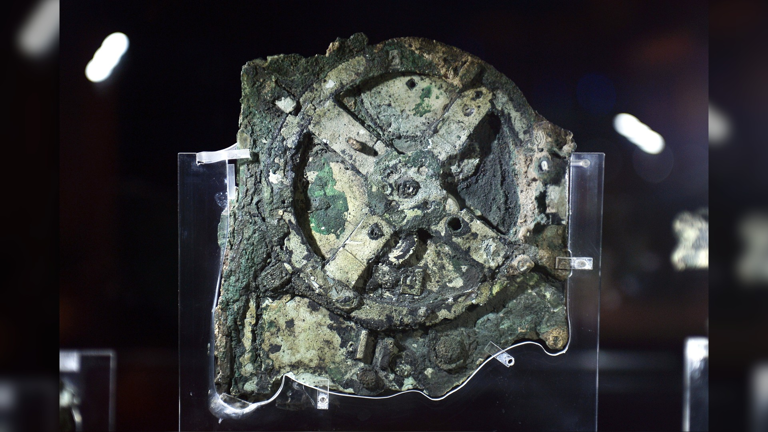
Unearthed from a shipwreck in Greece in 1901, the Antikythera Mechanism has remained a source of fascination for computer experts for centuries. This manually operated device was an extraordinary timekeeping instrument, utilizing an intricate winding system to meticulously track the movements of the sun and planets. It also served as a calendar, accurately monitoring lunar phases and eclipses.
Although its concept may appear deceptively simple, the Antikythera Mechanism was remarkably advanced for its time, surpassing any other tool or invention for the subsequent thousand years. However, due to the incomplete preservation of the device (consisting of 30 corroded bronze gearwheels and 82 fragmented pieces), researchers have grappled with understanding its look and abilities.
Though past investigations had managed to decipher the rear section of the Antikythera Mechanism, the intricate gearing system located at the front had remained an enigma. However, a recent breakthrough was made by scientists from University College London.
Utilizing advanced 3D computer modeling techniques, they successfully reconstructed the complete front panel, providing valuable insights into the intricate details and complex components of the device.
With this significant progress, the researchers now aim to take their work further by constructing a full-scale replica of the Antikythera Mechanism using modern materials. Adam Wojcik, a materials scientist at UCL, expressed their confidence in the reconstruction, stating, “We think that our reconstruction aligns with all the collected evidence gathered by scientists from the surviving fragments up to this point.”
In addition, the researchers proposed a theory regarding the functionality of the device. They hypothesized that the Antikythera Mechanism tracked the movements of the sun, moon, and planets using concentric rings, reflecting the ancient Greek belief that these celestial bodies orbited the Earth.
Describing their findings in a paper published in Scientific Reports, the researchers stated, “Unraveling this intricate 3D puzzle unveils a remarkable creation that merges cycles from astronomy in Babylon, mathematical principles from the Academy of Plato, and astronomical theories from the ancient Greeks.”
Professor Tony Freeth, the lead author of the paper, expressed admiration for the device’s representation of the galaxy. He described it as an extraordinary display of ancient Greek ingenuity, stating, “Our model is the very first that aligns with all the physical evidence and corresponds to the descriptions found in the device’s engraved scientific inscriptions.”
The Antikythera Mechanism was originally contained within a wooden box and comprised of an intricate arrangement of dials, gears, and inscriptions. It is estimated to have been crafted between 150-100 BCE. Initially, following its discovery, the mechanism was mistakenly believed to be a mere decorative object for many years. However, through meticulous analysis, researchers gradually unraveled its significant intricacy.
All known fragments of the Antikythera Mechanism are currently housed at the Athens National Archaeological Museum alongside replicas and artistic reconstructions that offer insights into its potential appearance and functionality. The device serves as a testament to the advanced level of sophistication achieved by ancient civilizations, challenging the notion that computers are exclusive to the modern era.
In addition to the Antikythera Mechanism, there are several other remarkable ancient computing devices that have made a lasting impact on human history. One such device is the Astrolabe, which proved instrumental for navigators and astronomers in determining celestial positions. The Baghdad Battery remains an enigmatic artifact that suggests ancient knowledge of electricity. Furthermore, Charles Babbage’s Difference Engine and Analytical Engine played a pivotal role in laying the groundwork for modern computing.
These ancient devices, including the Antikythera Mechanism, serve as compelling reminders of humanity’s unwavering quest for knowledge. They continue to inspire us by bridging the gap between the technological advancements of the past and present, showcasing the ingenuity and innovation that has shaped our journey of discovery.
Who knows? Maybe in 2,000 years, someone will unearth your iPhone with the same level of excitement at having discovered an ancient relic.