Scientists have made a remarkable discovery deep within the Earth’s crust, uncovering a fascinating geological feature that has been likened to, well, Hell.
Is this a mystical realm of fire and eternal doom?
Not exactly, though at a glance, it looks pretty close.
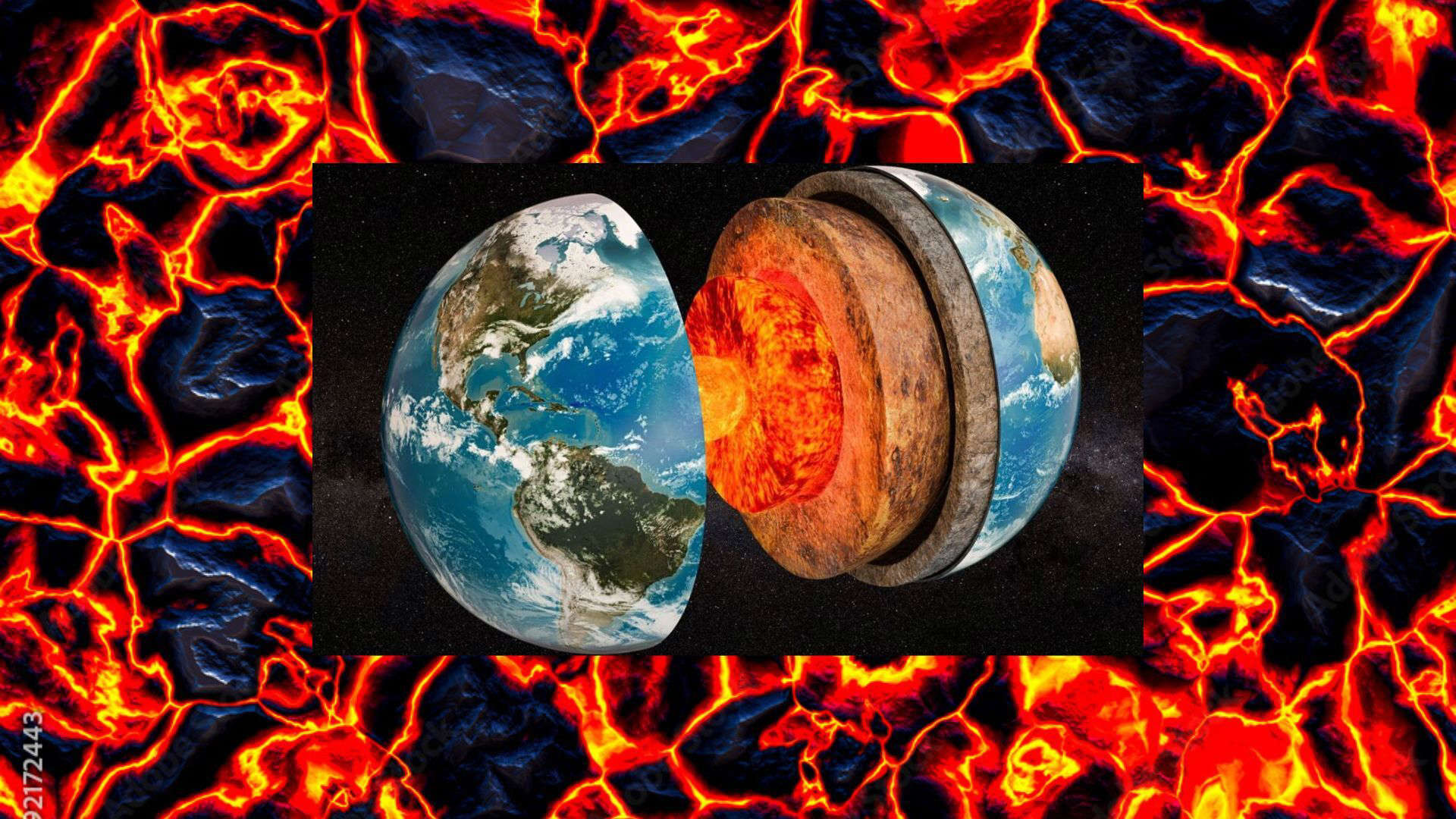
In a recent publication in the scientific journal Nature Geoscience, scientists from the University of Texas have unveiled a remarkable finding—an underlying layer of molten rock located beneath Earth’s tectonic plates. This incredibly hot zone, situated approximately 100 miles beneath the surface, reaches temperatures exceeding 2,600 degrees Fahrenheit.
Previous scientific understanding suggested that molten melt existed in isolated regions. However, recent discoveries have shed light on the global presence of this molten layer and its significant connection to plate tectonics. This layer is a component of the asthenosphere, located beneath Earth’s tectonic plates in the upper mantle. It provides essential topography and forms a relatively pliable boundary that enables the movement of these plates through the mantle. Without this pliability, the upper layers of the Earth would be excessively rigid, hindering the dynamic motion of tectonic plates.
According to Junlin Hua, the lead researcher from the University of Texas Jackson School of Geoscience, the prevailing notion suggests that a high concentration of melt would significantly impact the viscosity of the material. However, the recent findings indicate that despite the presence of a substantial melt fraction, its influence on the flow of the mantle is relatively insignificant. Hua explains that the melt’s role in mantle flow is not as pronounced as initially anticipated, challenging previous intuitions regarding its viscosity-related effects.
The study reveals that the motion of tectonic plates is primarily influenced by the heat and rock present in the mantle, diminishing the significance of the molten layer. Despite the predominantly solid nature of Earth’s interior, the rocks have the ability to gradually shift and flow akin to the viscosity of honey over extended periods. This highlights the dynamic nature of the Earth’s interior and the continuous movement of its geological features.
According to coauthor Thorsten Becker, the melt layer does not play a significant role in plate tectonics. Instead, it is considered more of a byproduct or consequence of the processes occurring beneath the surface of the Earth. The presence of the melt layer is an outcome of the Earth’s internal dynamics, rather than a driving force behind plate tectonics.
Co-author Esteban Gazel, from Cornell University, emphasizes the significance of the study, stating that it provides a deeper comprehension of the planet’s internal dynamics. Furthermore, the research sheds light on the physical properties of the boundary layer, which is crucial for various aspects, including the existence of life on Earth. The study’s findings contribute to a broader understanding of Earth’s intricate systems and their relevance to the overall functioning of our planet.
The discovery of the underlying molten layer beneath Earth’s tectonic plates has sparked new avenues of research and exploration. Scientists are now focused on understanding the composition and behavior of this molten rock and its implications for Earth’s geology.
One area of investigation is the study of magma chambers and their connection to volcanic activity. The molten layer provides a potential source of magma that can rise to the surface during volcanic eruptions. By examining the characteristics of the molten layer and its interaction with the overlying tectonic plates, scientists aim to improve volcanic eruption forecasting and hazard assessment.
Furthermore, the discovery has implications for the study of Earth’s ancient geological history. The molten layer may preserve a record of past tectonic processes and plate movements. By analyzing the composition and isotopic signatures of rocks derived from the molten layer, scientists can gain insights into the Earth’s geological evolution over millions of years.
The molten layer’s influence extends beyond the solid Earth. It plays a crucial role in the generation of Earth’s magnetic field, which protects our planet from harmful solar radiation. Understanding the interaction between the molten layer and the core is essential for unraveling the mysteries of Earth’s magnetic field and its long-term stability.
Moreover, the newfound knowledge of the molten layer has implications for the search for life beyond Earth. The movement of tectonic plates, driven by the underlying molten layer, is a key factor in the recycling of nutrients and the regulation of surface conditions that support diverse ecosystems. By studying the molten layer, scientists can gain insights into the potential habitability of exoplanets and moons in our cosmic neighborhood.
The discovery of this molten layer beneath Earth’s tectonic plates opens up a world of possibilities for scientific inquiry and exploration. It is a testament to the never-ending curiosity of humankind and our relentless pursuit of knowledge about the planet we call home. As researchers delve deeper into the mysteries of the molten layer, we can expect even more profound discoveries that will shape our understanding of Earth and its place in the cosmos.