Neptune’s Clouds Are Gone Thanks to the Sun: Are Earth’s Clouds the Next to Go?
According to recent research, Neptune’s famous clouds are all but gone. Although no one knows for sure what has happened to the Blue Planet’s clouds, the most believed hypothesis is that the sun is to blame.
Scientists believe that the changing patterns and rotation of the sun have led to the new surprisingly clear skies on Neptune.
How the Sun Moves
Before understanding how the sun is affecting Neptune, it’s first important to learn exactly how our sun moves.

Source: Mario Tama/Getty Images
The sun in our solar system has an 11-year cycle. That means that every 11 years, the sun’s magnetic poles switch; the north becomes the south pole and vice versa. While the electromagnetic poles transition from one side to the other, large amounts of ultraviolet radiation are released.
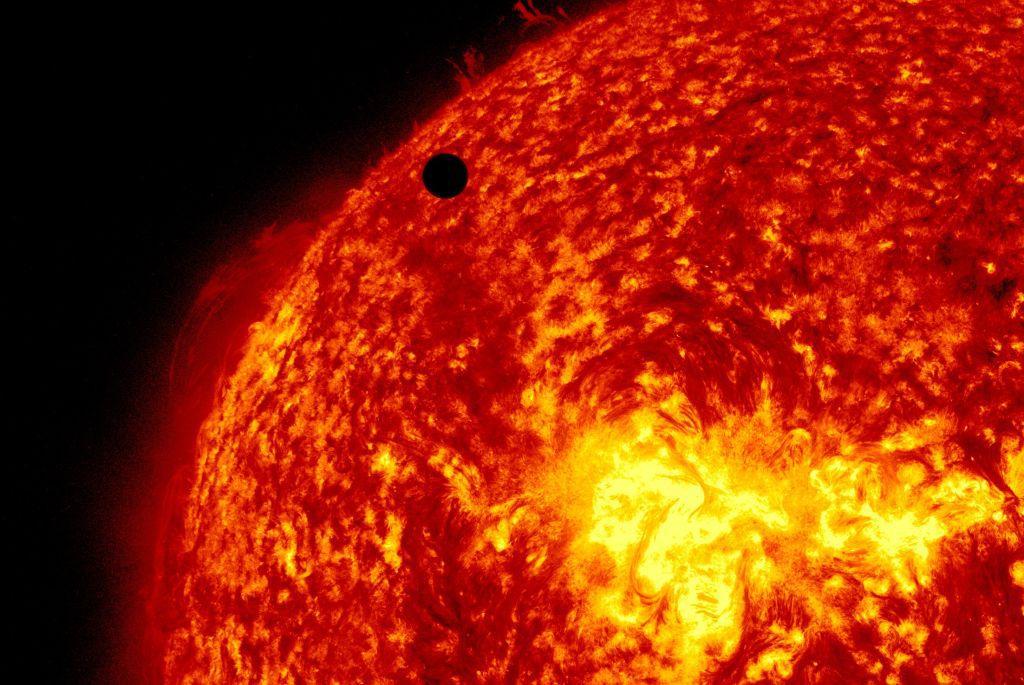
The Plasma Particles on the Sun Are Actually Moving
Here’s how it works: Essentially, our sun is a big ball of charged plasma particles that flow in a circular motion. These plasma particles that make up the sun’s surface move causes the pole rotation and directly affects the sun’s magnetic cycles.

Source: SDO/NASA/Getty Images
And because certain areas on the sun’s surface have more intense solar flares, depending on the sun’s rotation, the planets in our solar system receive more intense ultraviolet radiation.
The Sun’s Rotation Affects Our Technology
The frequent intense solar flares of the sun’s plasma create what scientists call “magnetic knots.” These knots can cause problems for the Earth’s satellites orbiting in space.

Source: Joe Raedle/Getty Images
The magnetic knots can also spew solar plasma, and while humans cannot directly feel the plasma, the charged particles that reach the Earth’s atmosphere can actually cause problems with communication devices
The Sun’s Rotation Affects Every Planet in the Solar System
In addition to affecting human-made technology, the solar flares, magnetic knots, and plasma particles also directly influence the planets throughout the solar system.
Source: Alamy
When these cycles of the sun occur, greater amounts of ultraviolet radiation are spread throughout the solar system, which leads to more light energy. However, this intense light from the sun doesn’t actually reduce cloud cover on planets such as Neptune, it increases it.
Neptune Cloud Research
Of course, there is an immense amount of research about our own planet Earth, but several astrophysicists have been focusing their attention on the other planets, including Neptune, for years in order to better understand the solar system as a whole.

Source: Alexander Gerst/ESA/Getty Images
In fact, detailed research of Neptune’s clouds has been ongoing. The data shows that the planet experienced almost clear skies in 2007 and 2020, and extremely cloudy skies in 2002 and 2015.
Neptune’s Clouds Are Based Directly on the Sun’s Rotation
Because Neptune is 2.7 billion miles from the sun, it takes two years for the sun’s UV radiation to arrive at the Blue Planet and directly impact its atmosphere.
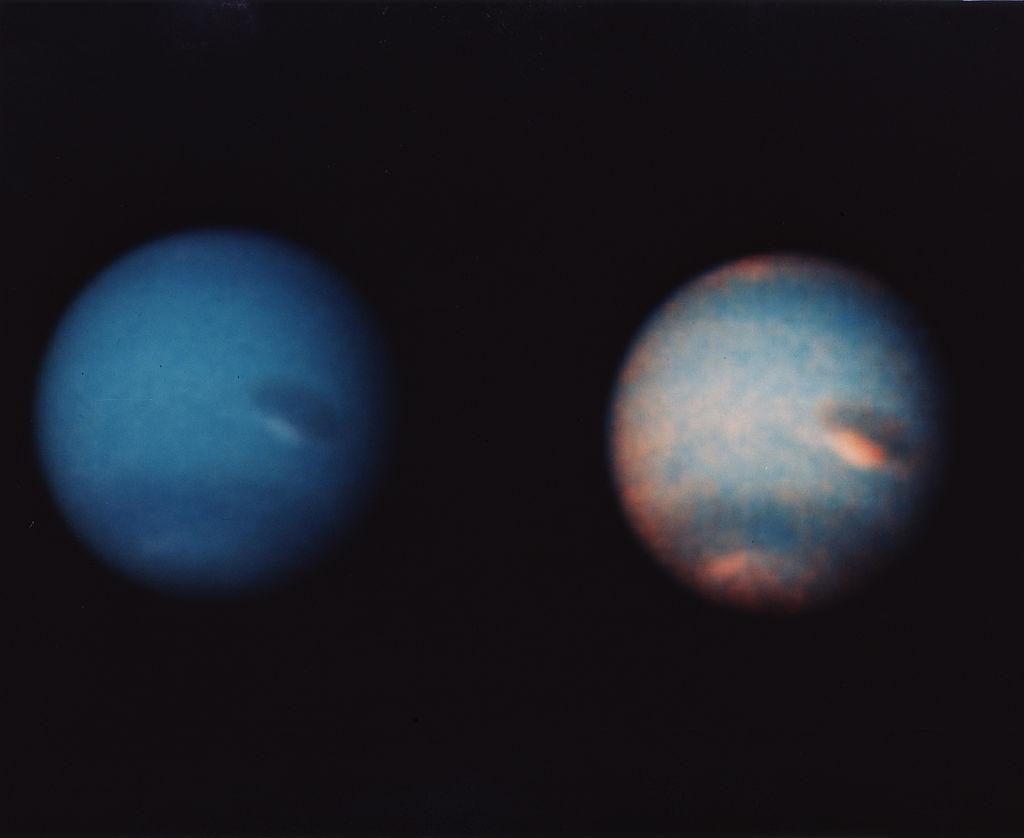

Source: Corbis/Getty Images
And as scientists now understand, the more intense the solar power from the sun, the more clouds they see on Neptune. That means that two years after a “solar peak,” there will be a boost in cloud coverage on the Blue Planet.
Analysis of Neptune’s Cloud Coverage
According to the research, Neptune had an incredible amount of cloud coverage in 2002, and then very little in 2007. The five year cycle continued and scientists saw the same in 2015 and 2020, respectively.

Source: Robert Alexander/Getty Images
However, from 2008-2009, in the two years after Neptune’s reported low coverage in 2007, scientists saw the clouds returning slowly but surely, which doesn’t seem to be happening this time around.
Neptune Has Had Little to No Cloud Cover Since 2020
Researchers are surprised and slightly concerned to see that Neptune’s cloud coverage, which was at an all time low in 2020, has yet to return to normal.
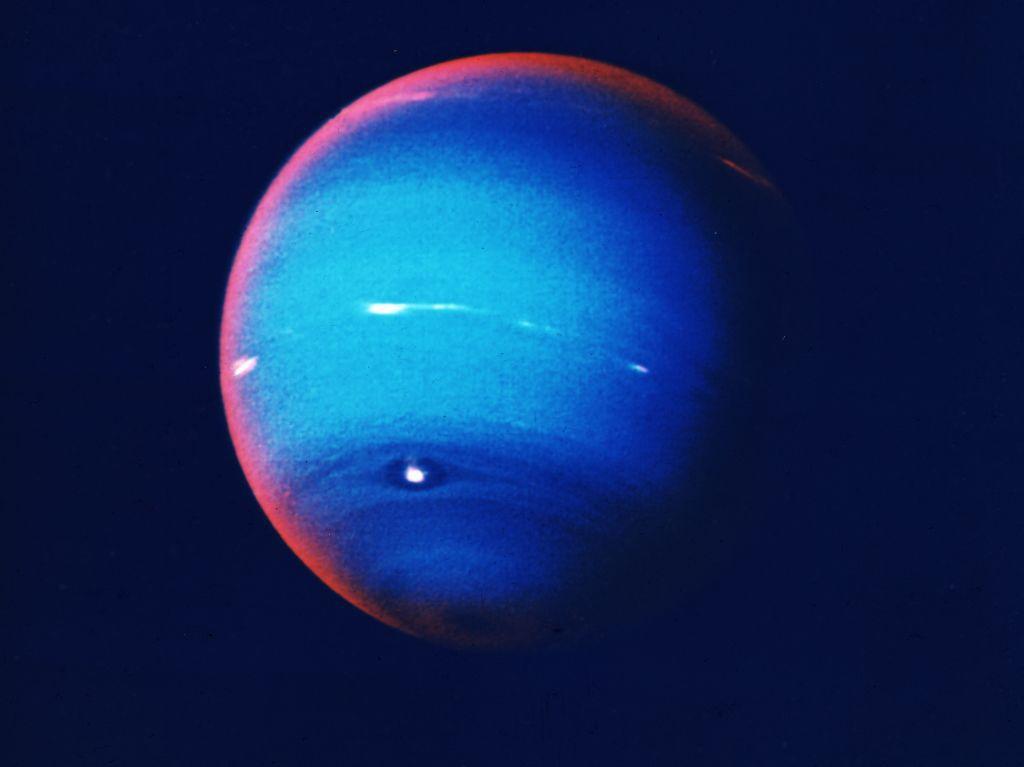

Source: Nulton Archive/Getty Images
In fact, in the many years that scientists have been observing the clouds of the Blue Planet, this is the longest time period on record with such little cloud coverage. While no one knows for sure if the sun is to blame, the ongoing research has made it the most likely theory.
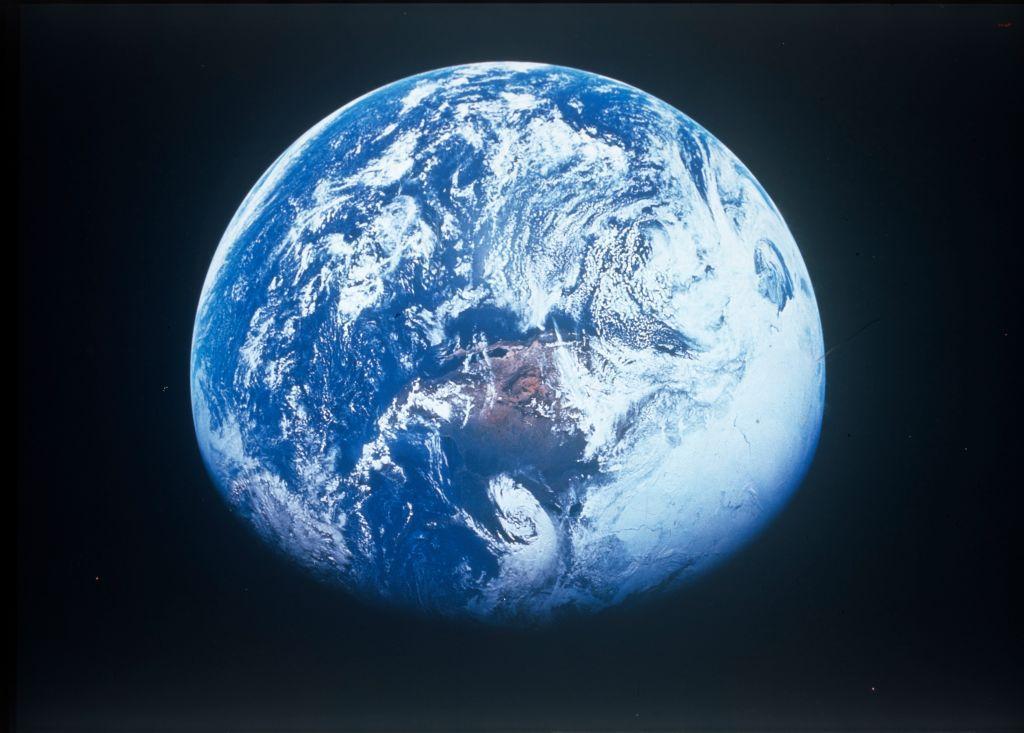
Earth Is Absolutely Affected by the Sun
Planet Earth is much closer to the sun than Neptune. We live only 93 million miles away from the burning star, as opposed to Neptune’s 2.7 billion miles.

Source: Heritage Images/Getty Images
But while meteorologists and scientists have certainly known for centuries that the sun affects our cloud coverage and weather patterns, the detailed research being performed today has shed light on just how drastically the sun’s rotation can lead to fewer clouds, strong trade winds, and rainfall.
Are Earth’s Clouds the Next to Go?
Many who learn about the phenomenon of Neptune’s disappearing clouds have asked themselves: Are Earth’s clouds the next to go?

Source: Space Frontiers/Getty Images
Without clouds, our planet, atmosphere, and environment would change drastically. And while based on the research, scientists now know that the 11-year solar cycle does affect cloud coverage, no data collected has pointed to the idea that Earth will soon be cloudless.
Can This Research Affect How We Understand Climate Change?
So far, no connections have been made in the media between the sun’s current rotation, magnetic cycle, and UV radiation to our planet’s current extreme weather and climate change problem.

Source: Roger Anis/Getty Images
However, scientists are hopeful that studying what’s happening to Neptune’s clouds will help them better understand exactly how the sun affects all the planets in our solar system, including the one we all live on.
